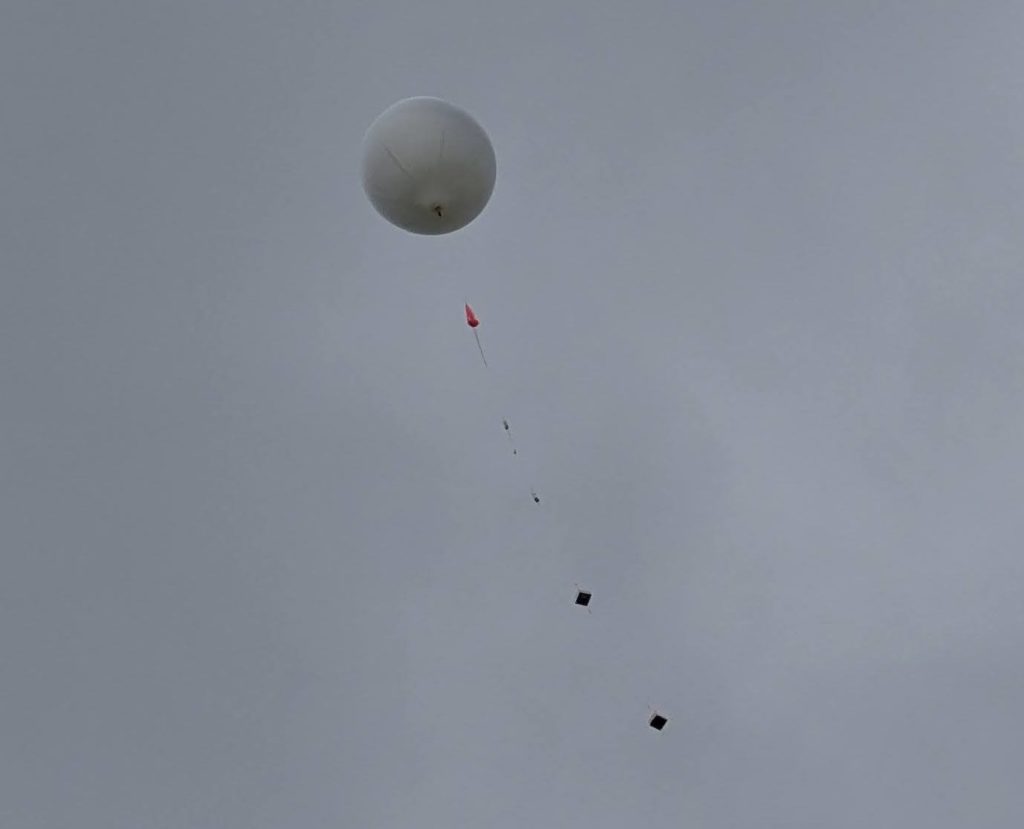
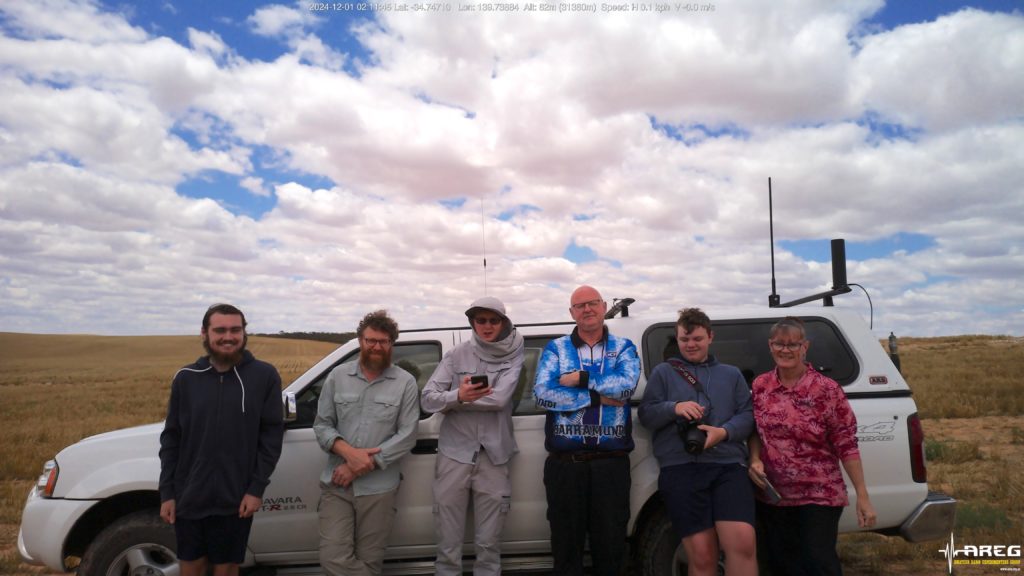
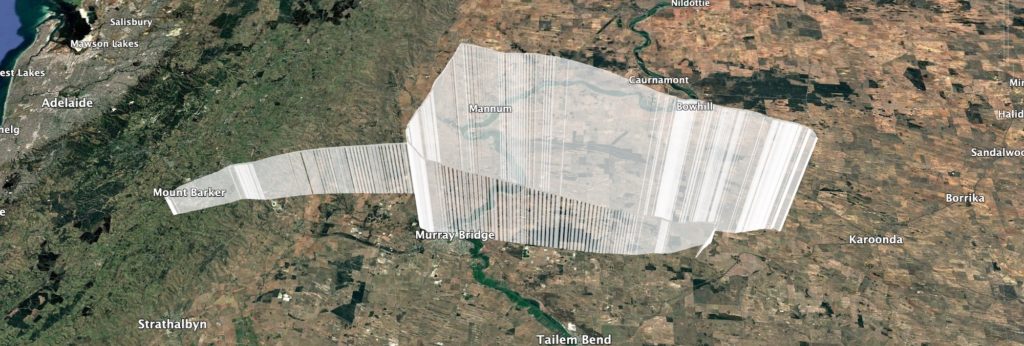
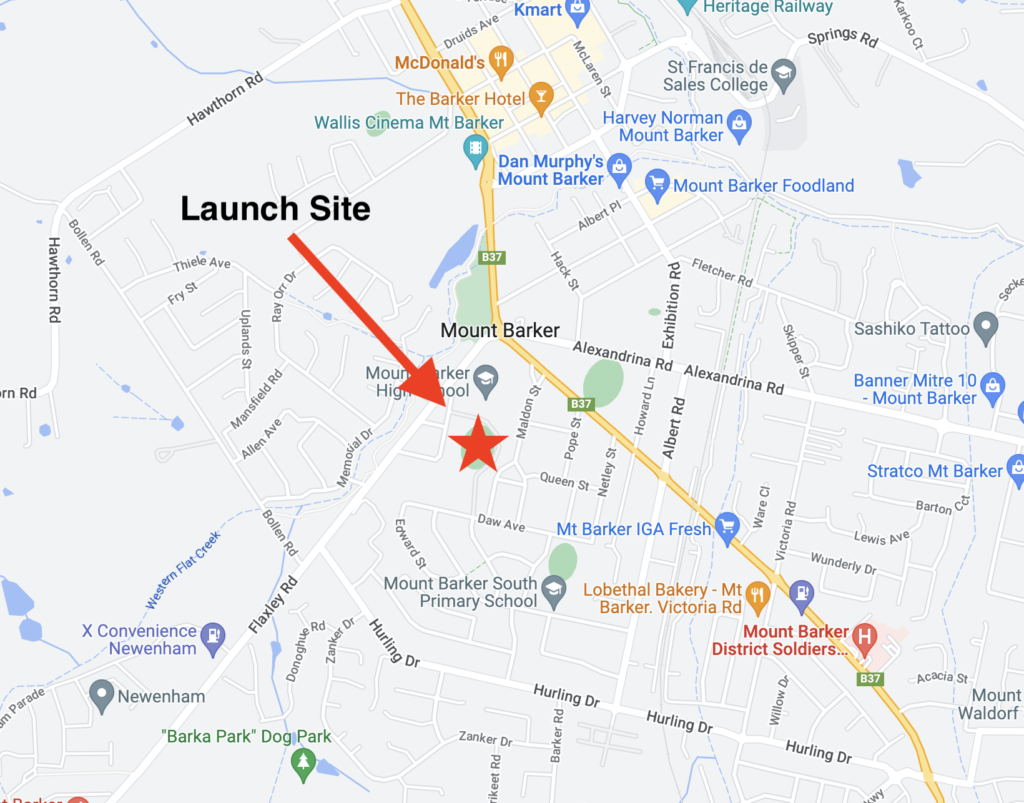
Project Horus’s 69’th flight was held on the 18th of January 2026, launching from our usual launch site, the Mt Barker High School oval. This flight was a test of a few new and experimental payloads, including our first flight of the new ‘Horus Binary v3’ tracking telemetry mode.
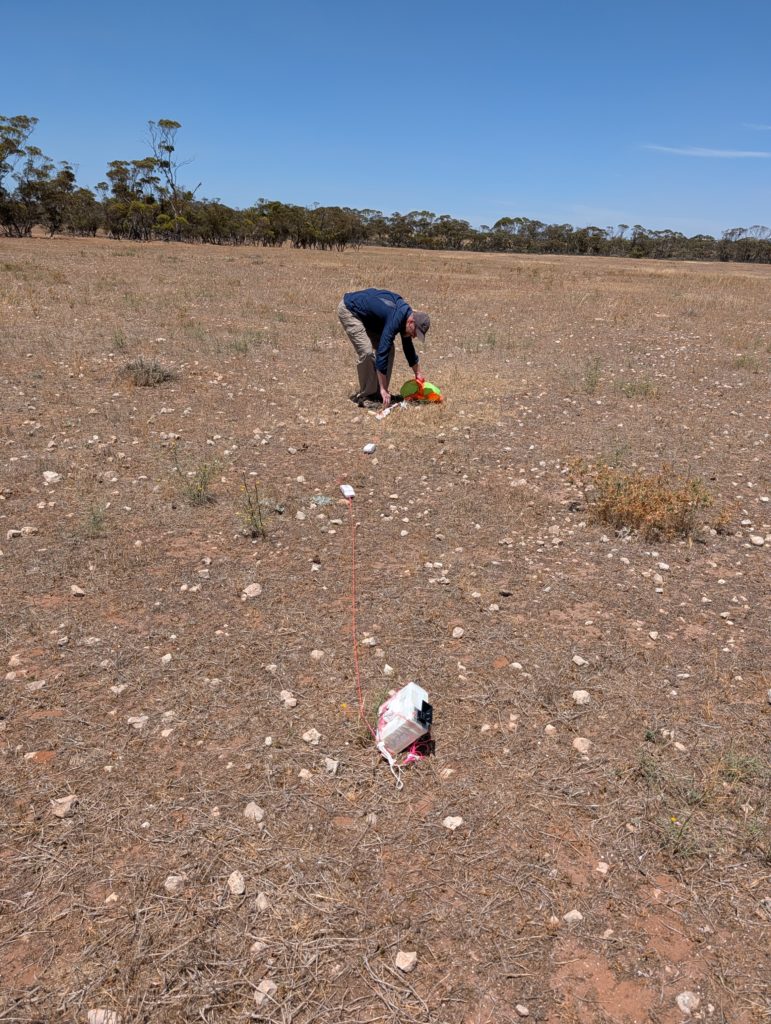
The launch was an easy one, with only light winds at the launch site. It was great to see a few new faces along to see what a high-altitude balloon launch is all about!
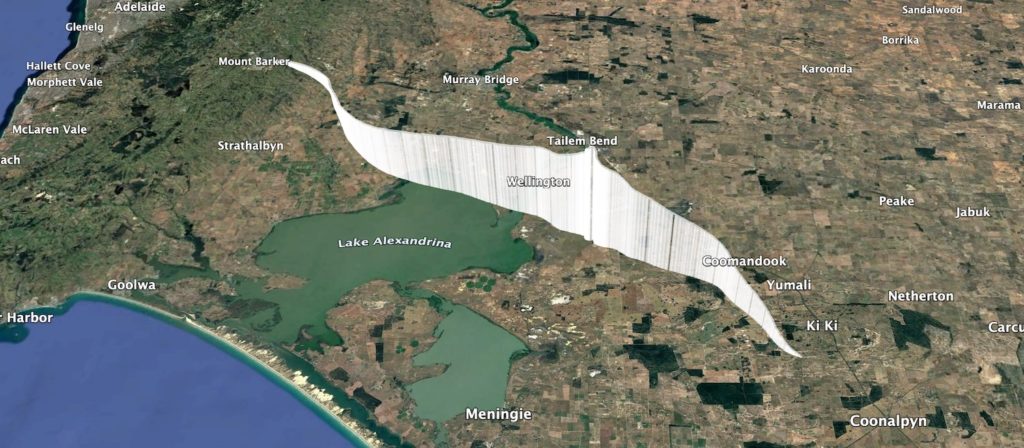
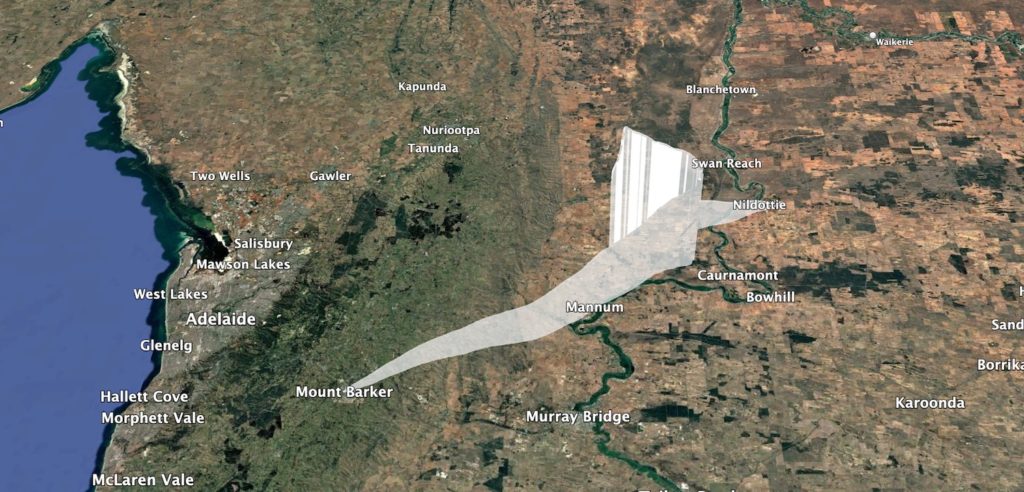
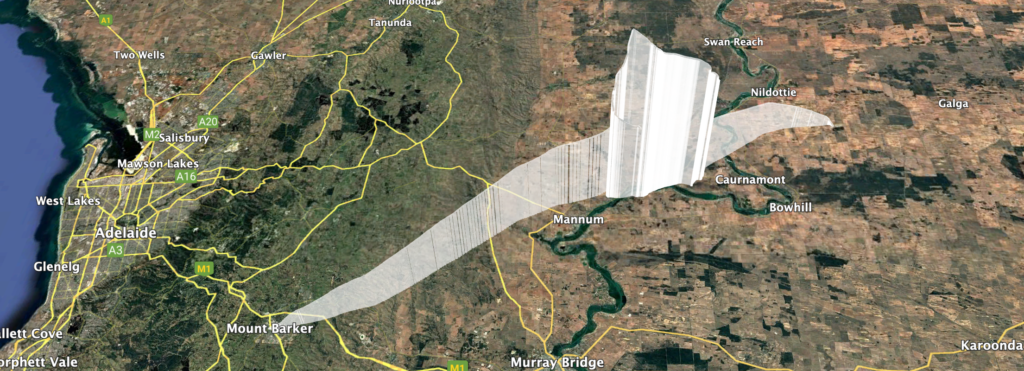
The predicted flight path allowed for a fairly relaxed chase, so the chase teams headed off to Tailem Bend for some lunch while waiting for the balloon rise closer to its expected burst altitude. Chasing the flight were Mark VK5QI. Will VK5AHV, Autumn VK5CLD, and Peter VK5APR. We also had Peter VK5KX and Matt VK5ZM set up near Palmer tracking the flight.
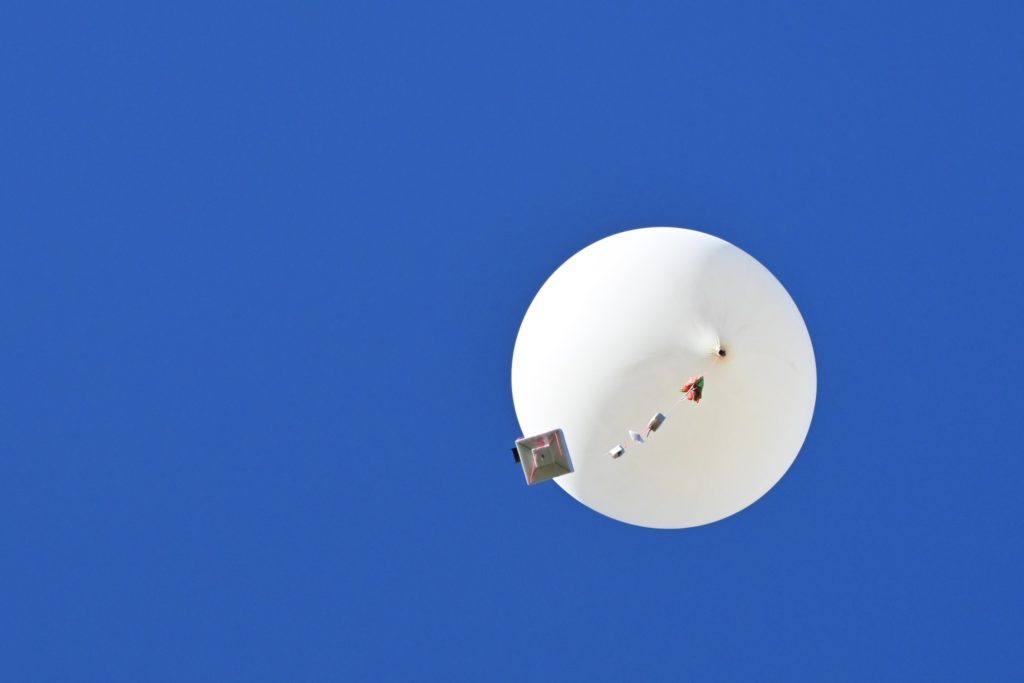
The balloon ended up bursting at 33.831km altitude, a good 3 km higher than expected! The payloads descended to a landing approximately 20km north-east of Tailem Bend, just off the Karoonda highway. A quick chat to the landowner, and the chase teams were able to drive right up to the landing spot! A big thanks to Wayne Gregory for being so helpful!
Horus 69 Flight Statistics
| Launch Date: | 2026-01-17T23:26:31Z |
| Landing Date: | 2026-01-18T02:04:16Z |
| Launch Site: | -35.07579, 138.85710 |
| Landing Site: | -35.13652, 139.62709 |
| Distance Travelled: | 70 km |
| Maximum Altitude: | 33831 m |
Horus v3 Payload – HORUS-V3
This was the first Australian flight of the Horus Binary v3 telemetry mode, the latest version of the Horus Binary high-altitude balloon flight tracking system.
The following stations received the Horus v3 telemetry on this flight: BARC_4, VK3APJ, VK5ARG, VK5GA, VK5GA-2, VK5GY, VK5KX-9, VK5KX-i5, VK5QI-1, VK5QI-9, VK5SFA/R, VK5ST-5, VK5ZM
A dashboard showing reception statistics for this payload are here: https://grafana.v2.sondehub.org/goto/BBkF1dIvR?orgId=1
Thanks to everyone that updated their decoding software and had a go at decoding this new format! Based on the success of this flight (and many other flights overseas), Horus v3 will become the primary tracking mode used on future Project Horus flights.
Horus v2 Payload – HORUS-V2
While we will be switching to Horus v3 in the future, this flight still used a Horus v2 payload as the primary tracking payload, and we thank everyone that helped out with tracking on this flight:
BARC_4, VK3APJ, VK3BQ, VK5AKK, VK5AKK-1, VK5ARG, VK5BL, VK5BRL, VK5BTN, VK5CLD-9, VK5CV, VK5DJ, VK5GA, VK5HW, VK5KX-9, VK5LN, VK5MAS, VK5NEX, VK5OCD, VK5QI-9, VK5RA, VK5RM, VK5ST-5, VK5TRM, VK5ZAR, VK5ZM, VK5ZMD, VK5ZRL, VK5ZRL-2, VK5ZRL/2, vk5is
A dashboard for the Horus v2 payload is available here: https://grafana.v2.sondehub.org/goto/szhKJOSvR?orgId=1
Wenet Imagery Payload
The imagery payload on this flight was another experiment with the PiCam v3 autofocus camera, using information gained from flights in the United States that were successful in taking good quality (and importantly, in focus!) imagery. Thanks to the following stations that received imagery from this payload:
- VK3APJ: 8410 packets (2.05 MB)
- VK5QI-9: 186131 packets (45.44 MB)
- VK5KX-9: 238707 packets (58.28 MB)
- VK5CLD-9: 64276 packets (15.69 MB)
- VK5IS: 51247 packets (12.51 MB)
A dashboard for the Wenet payload is available here: https://grafana.v2.sondehub.org/goto/A80OJOIvg?orgId=1
Sadly, the dynamics of the payloads on this flight (swinging + spinning) meant that the autofocus algorithm just couldn’t keep up, again resulting in blurry imagery. This is likely the final nail in the coffin for this camera unless we can work out a way of stabilising the payload without adding lots of extra mass. Work has now started on updating the ‘PiCam HQ’ payload (which last flew on Horus 60) up to the Wenet v2 standard, and this will likely fly on the next full launch.
A selection of photos from the payload are shown below:
Next Launch
Our next ‘full size’ launch will likely not be until the weather cools down again in March, and hopefully we’ll be able to finally get the Cross-band repeater in the air. Before then there may be some small launches with just Horus Binary v3 payloads, to assist receiving stations in getting their software updated and tested.
Again, thanks to everyone that participated in the launch, and we hope to see you on the map on our next flight!